Bidirectionality of language contact: Spanish and Catalan vowels
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
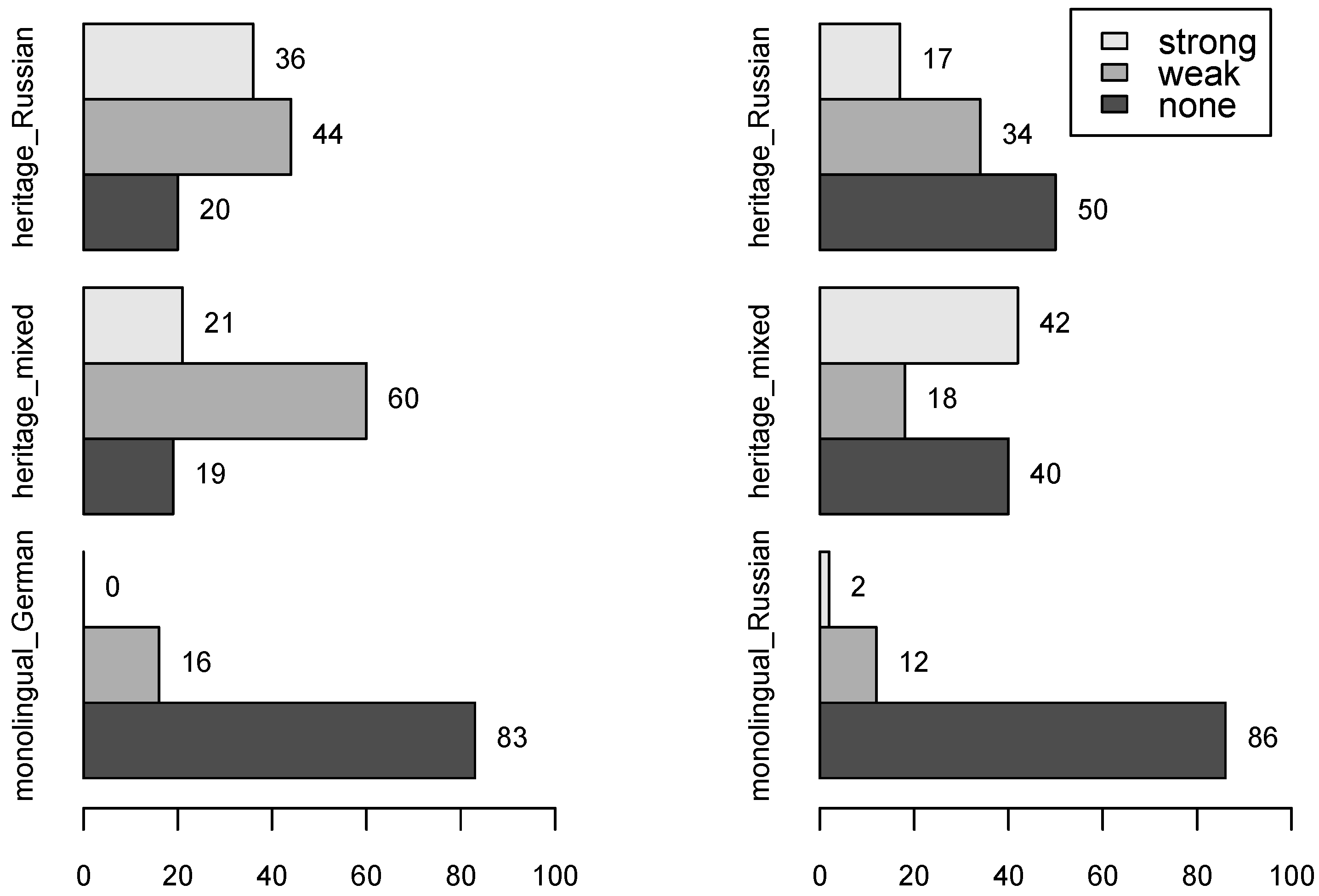
The disproportionate number of studies in Barcelona and the Balearic Islands observing Spanish contact effects in Catalan production, rather than Catalan contact effects in Spanish production, is an oversight of bidirectionality and the probabilistic nature of social factors in situations of language contact. Accordingly, the present study analyzes both Catalan and Spanish mid front vowel production data from Barcelona to investigate whether Catalan contact effects occur in Spanish via a process of dissimilation, and whether such effects are strengthened in younger speakers due to the relatively recent implementation of Catalan linguistic policy in the educational and public spheres. The results are suggestive of dissimilation, where phonetic distinctions are maintained between Spanish /e/ and the two Catalan mid front vowels across both F1 and F2. Additionally, analyses of variance across F1 and F2 reveal that Spanish /e/ productions across F1 are more diffuse in younger speakers and Catalan mid front vowels across F2 are less diffuse, providing evidence of reciprocity in contact effects. These results underscore the bidirectional nature of language contact and advocate for the use of variance of F1 and F2 as a metric of phonological contact effects.
Languages, Free Full-Text

PDF] The interlingual identification of Spanish and English vowels

Mixed language processing increases cross-language phonetic

The role of early experience and continued language use in

Language Contact Within the Speaker: Phonetic Variation and

PDF) Crosslinguistic influence in the acquisition of Greek as a
Navigating conflicting phonotactic constraints in bilingual speech
Aspects of the Phonology of Spanish as a Heritage Language: from

The role of early experience and continued language use in
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)






