Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Silk has a long history as an exclusive textile, but also as a suture thread in medicine; nowadays, diverse cell carriers are manufactured from silk. Its advantages are manifold, including high biocompatibility, biomechanical strength and processability (approved for nearly all manufacturing techniques). Silk’s limitations, such as scarcity and batch to batch variations, are overcome by gene technology, which allows for the upscaled production of recombinant “designed” silk proteins. For processing thin fibroin filaments, the sericin component is generally removed (degumming). In contrast to many synthetic biomaterials, fibroin allows for superior cell adherence and growth. In addition, silk grafts demonstrate superior mechanical performance and long-term stability, making them attractive for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tissue engineering. Looking at these promising properties, this review focusses on the responses of cell types to silk variants, as well as their biomechanical properties, which are relevant for ACL tissue engineering. Meanwhile, sericin has also attracted increasing interest and has been proposed as a bioactive biomaterial with antimicrobial properties. But so far, fibroin was exclusively used for experimental ACL tissue engineering approaches, and fibroin from spider silk also seems not to have been applied. To improve the bone integration of ACL grafts, silk scaffolds with osteogenic functionalization, silk-based tunnel fillers and interference screws have been developed. Nevertheless, signaling pathways stimulated by silk components remain barely elucidated, but need to be considered during the development of optimized silk cell carriers for ACL tissue engineering.

STEM CELLS: Vol 35, No 5
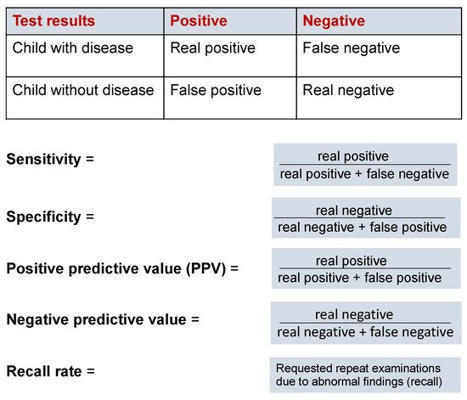
Cells, Free Full-Text

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy
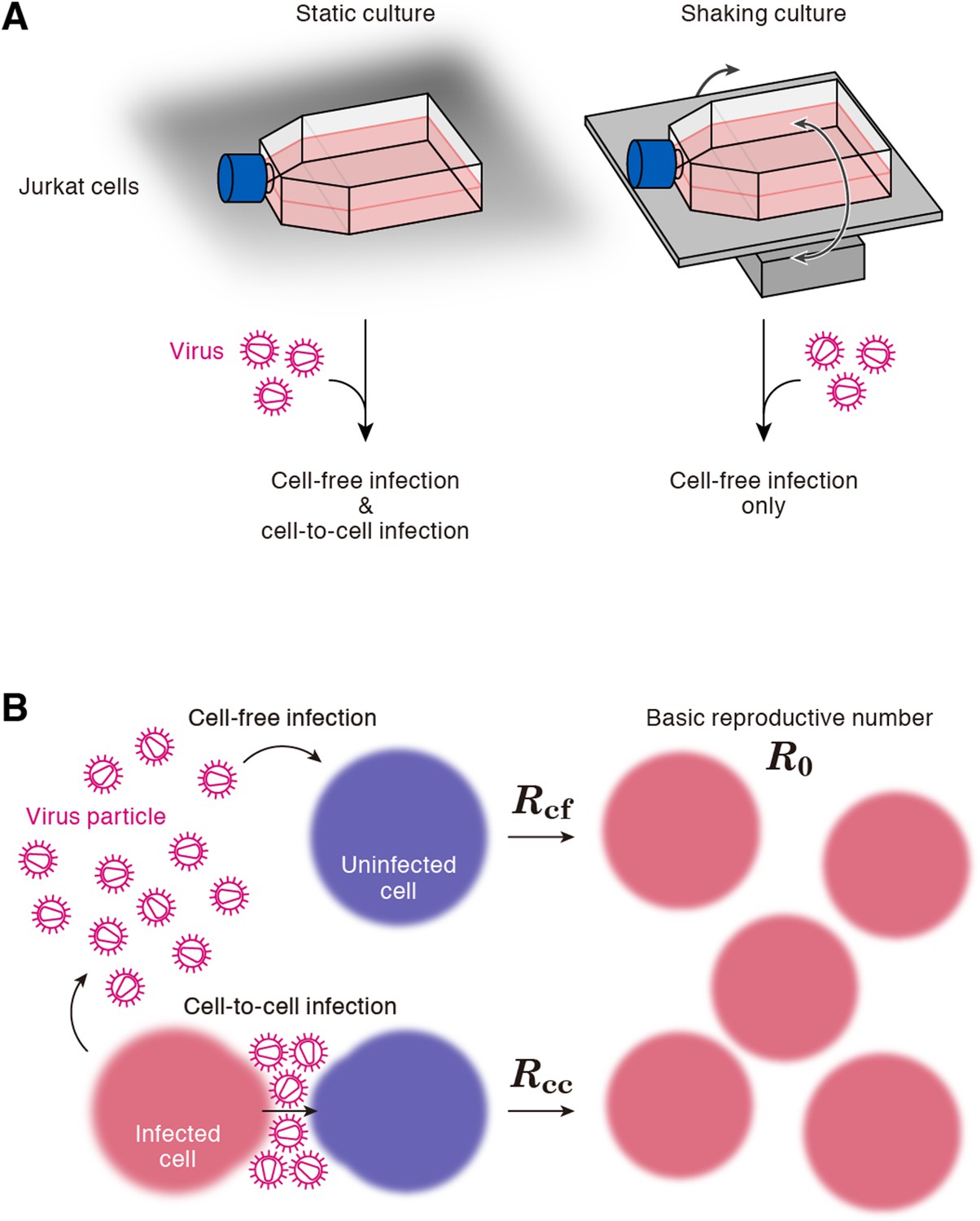
Cells, Free Full-Text
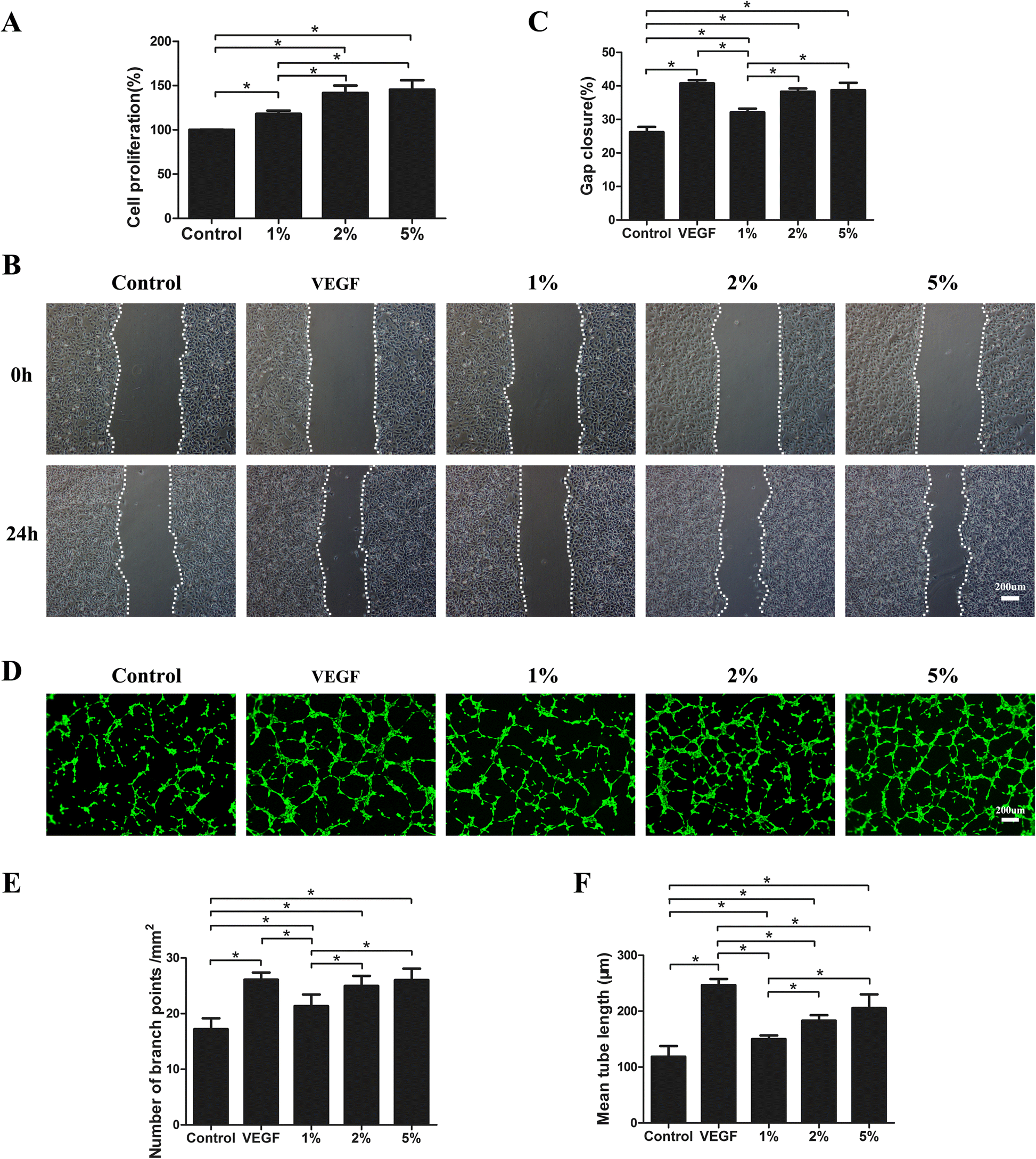
Fat extract promotes angiogenesis in a murine model of limb ischemia: a novel cell-free therapeutic strategy, Stem Cell Research & Therapy

Cells, Free Full-Text
Cell-Free Protein Expression
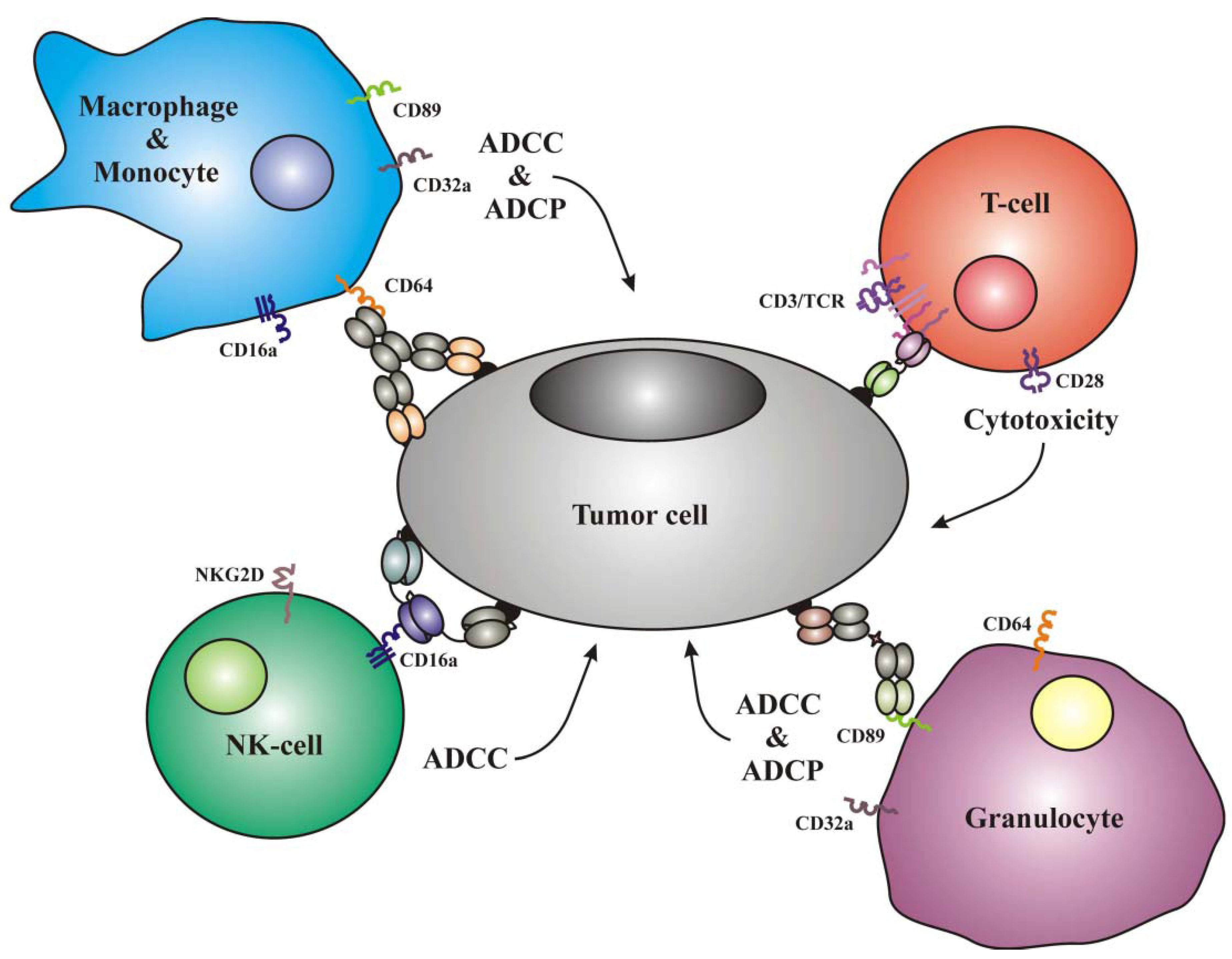
Antibodies, Free Full-Text
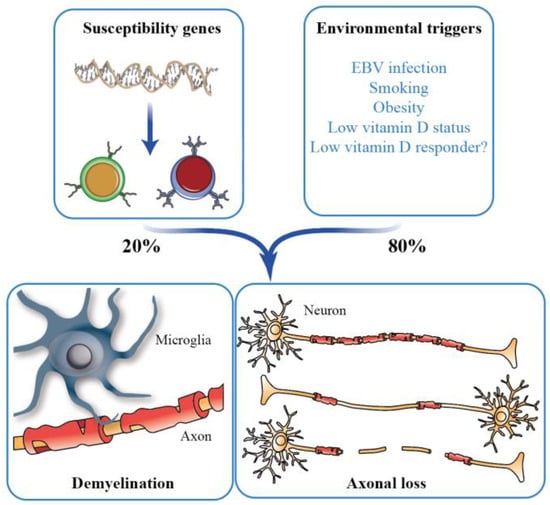
Oreilly Essential System Administration 3Rd Edition Aug 2002 Rar - Colaboratory

Circulating Tumor Cells, Disease Progression, and Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer
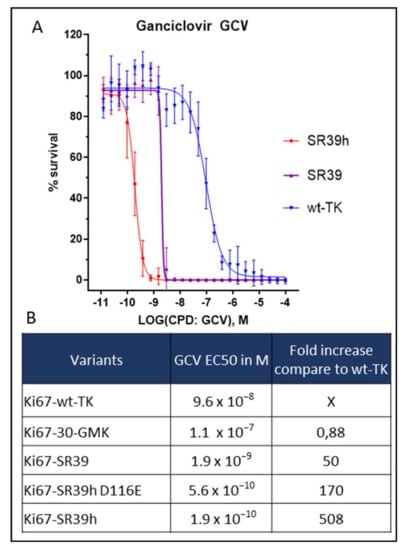
Serial Number Alcohol 120 1.9 6 - Colaboratory
The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Cells, Free Full-Text
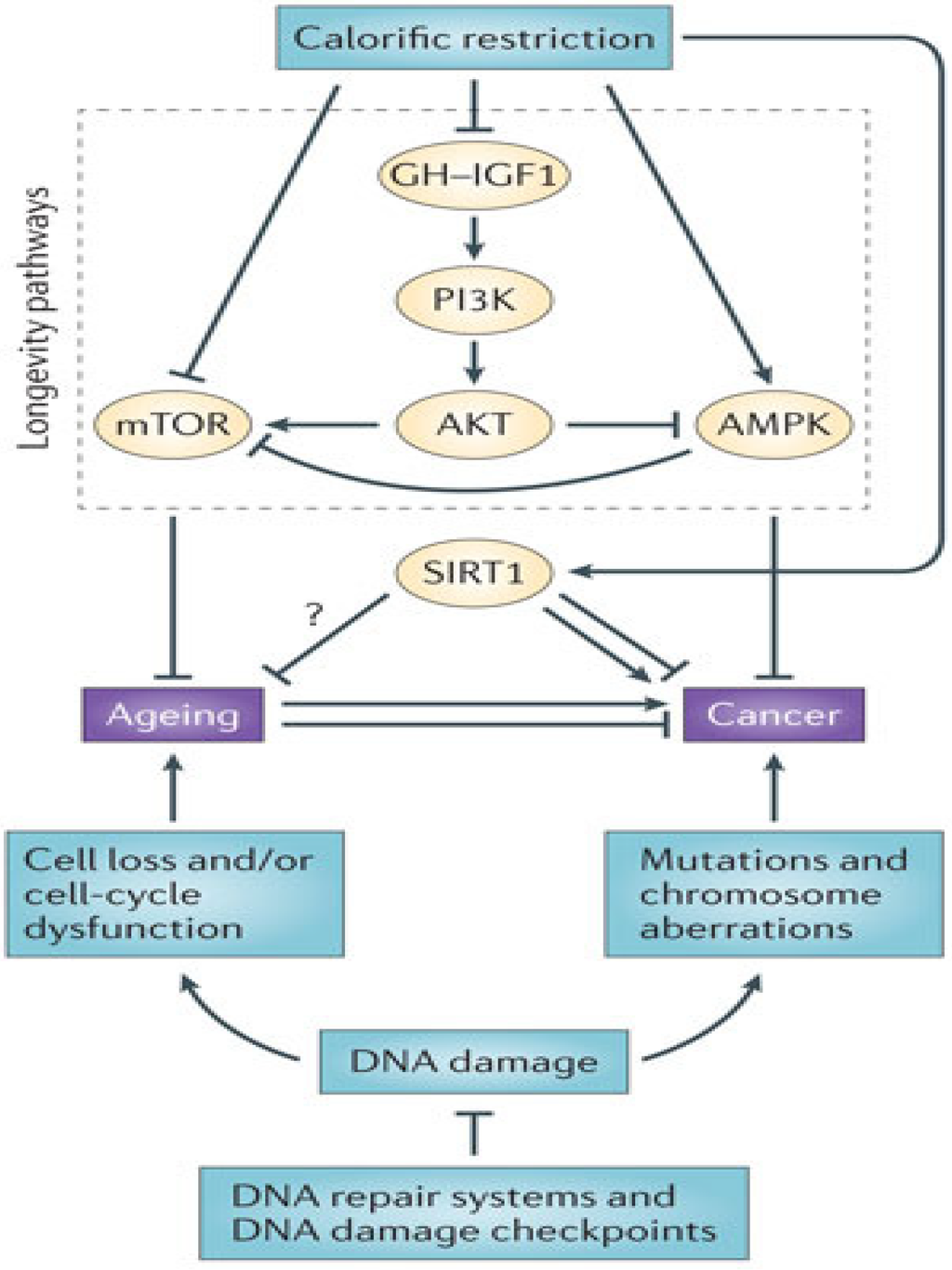
JCM, Free Full-Text
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)





