Biomechanical comparison of different prosthetic materials and posterior implant angles in all-on-4 treatment concept by three-dimensional finite element analysis
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
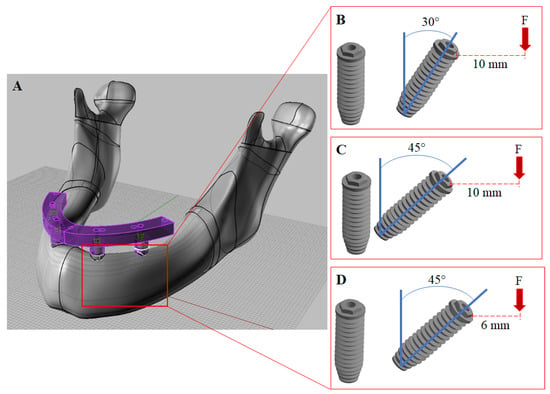
The study aimed to evaluate the biomechanical behaviors of different prosthetic materials and posterior implant angles in All-on-4 implant-supported fixed maxillary prostheses with three-dimensional (3D) finite element analysis. The model of complete edentulous maxilla was created using the Rhinoceros and VRMesh Studio programs. Anterior vertical and 17°- and 30°-angled posterior implants were positioned with All-on-4 design. Straigth and angled multi-unit abutments scanned using a 3D scanner. Two different prosthetic superstructures (monolithic zirconia framework and lithium disilicate veneer (ZL) and monolithic zirconia-reinforced lithium silicate (ZLS)) were modeled. Four models designed according to the prosthetic structure and posterior implant angles. Posterior vertical bilateral loading and frontal oblique loading was performed. The principal stresses (bone tissues-Pmax and Pmin) and von Mises equivalent stresses (implant and prosthetic structures) were analyzed. In all models, the highest Pmax stress values were calculated under posterior bilateral loading in cortical bone. The highest von Mises stress levels occured in the posterior implants under posterior bilateral load (260.33 and 219.50 MPa) in the ZL-17 and ZL-30 models, respectively. Under both loads, higher stress levels in prosthetic structures were shown in the ZLS models compared with ZL models. There was no difference between posterior implant angles on stress distribution occurred in implant material and alveolar bone tissue. ZLS and ZL prosthetic structures can be reliably used in maxillary All-on-4 rehabilitation.

PDF) Influence of Framework Material and Posterior Implant Angulation in Full-Arch All-on-4 Implant-Supported Prosthesis Stress Concentration

Evaluation of two treatment concepts of four implants supporting fixed prosthesis in an atrophic maxilla: finite element analysis, BMC Oral Health

Finite Element Analysis and Its Applications in Dentistry

Full article: Biomechanical comparison of implant inclinations and load times with the all-on-4 treatment concept: a three-dimensional finite element analysis

PDF) Biomechanical Comparison of Asymmetric Implant Configurations for All -on-Four Treatment Using Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis
Dentistry Journal, Free Full-Text
Comparison of stresses in monoblock tilted implants and conventional angled multiunit abutment-implant connection systems in the all-on-four procedure, BMC Oral Health

Biomechanical effect of implant design on four implants supporting mandibular full-arch fixed dentures: In vitro test and finite element analysis - ScienceDirect
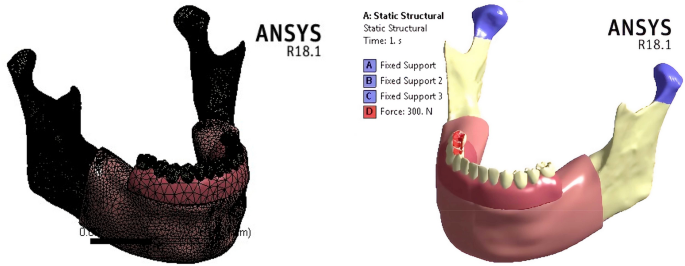
Evaluation of stress and strain on mandible caused using “All-on-Four” system from PEEK in hybrid prosthesis: finite-element analysis

Biomechanical effect of implant design on four implants supporting mandibular full-arch fixed dentures: In vitro test and finite element analysis - ScienceDirect

Strain in the cortical bone (A) and cancellous bone (B) around implants.

Full article: Biomechanical comparison of implant inclinations and load times with the all-on-4 treatment concept: a three-dimensional finite element analysis

10 11607@jomi 8122, PDF, Dental Implant

Effects of Different Positions and Angles of Implants in Maxillary Edentulous Jaw on Surrounding Bone Stress under Dynamic Loading: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis

Three-dimensional finite element analysis of two angled narrow-diameter implant designs for an all-on-4 prosthesis - ScienceDirect
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)