Cognitive profiles of children with autism spectrum disorder with parent-reported extraordinary talents and personal strengths
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The relationship between parent-reported talents and strengths and performance on standardized cognitive tests in 1470 children from the Simons Simplex Collection with autism and IQ above 70 is examined, highlighting the importance of exploring strengths separately by domain and a need for more research in this area. It is essential to recognize the strengths and talents of autistic individuals. Previous studies of extraordinary talents (i.e. skills that stand out relative to the general population) have combined individuals with different skills (e.g. calendrical calculation, drawing) into one group. There has been limited investigation of talents in specific areas and even less consideration of personal strengths (i.e. skills that stand out relative to that person’s other abilities, but not the general population). We extend this literature by examining the relationship between parent-reported talents and strengths and performance on standardized cognitive tests in 1470 children (4–18 years) from the Simons Simplex Collection with autism and IQ above 70. Almost half (46%) had at least one parent-reported talent and an additional 23% without extraordinary talents had at least one personal strength. Children with parent-reported talents and strengths had different cognitive profiles than children with no reported skill in visuospatial, drawing, computation, or music. Those highlighted for their memory abilities had somewhat more even verbal and nonverbal abilities, relative to children whose memory was not emphasized as a special skill. These results emphasize the importance of exploring strengths separately by domain and a need for more research in this area. Lay abstract Previous research has suggested that focusing on impairments can be detrimental to the well-being of autistic individuals, yet little research has focused on strengths and positive qualities in autism. Some studies explored “savant skills” (herein referred to as “extraordinary talents”), that is, skills that stand out compared to the general population. These often group everyone who has a specific talent, rather than exploring subgroups with strengths in specific areas. There has been even less research focused on personal strengths (i.e. skills that stand out relative to the individual’s other abilities, but not the general population). To expand this research, we use a sample of 1470 children (ages 4–18 years) from the Simons Simplex Collection without cognitive impairment to examine the relationship between having a parent-reported skill in a specific area and performance on a standardized cognitive test. Almost half (46%) had at least one parent-reported talent and an additional 23% without extraordinary talents had at least one personal strength. Children with these parent-reported skills had different patterns of performance on these standardized tests than children without skills in that area (i.e. visuospatial, drawing, computation, reading, and memory). Specific skills in computation or reading were associated with higher overall performance on the standardized tests. These results emphasize the importance of considering strengths separately by area, rather than combining individuals with different types of strengths. The high number of children with skills in this study underscores the need for more research in this area, particularly using instruments focused on understanding the nuances of these strengths. It is important for future studies to consider these skills in children with cognitive impairment.

Autism spectrum disorders in boys at a major UK hemophilia center: prevalence and risk factors - Research and Practice in Thrombosis and Haemostasis

The Association Between Autism Spectrum Disorder and Psychotic Experiences in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) Birth Cohort - Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry
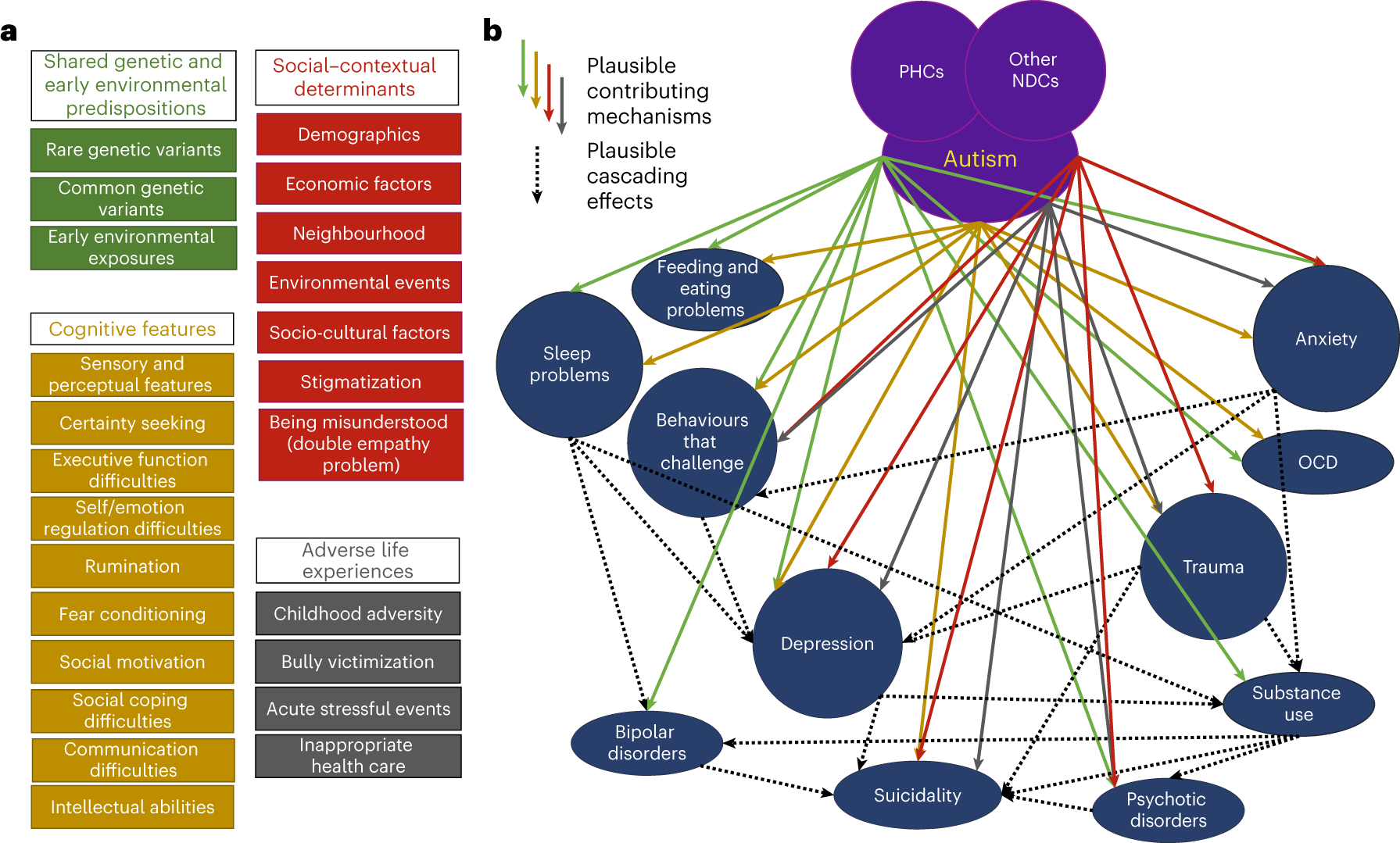
Mental health challenges faced by autistic people
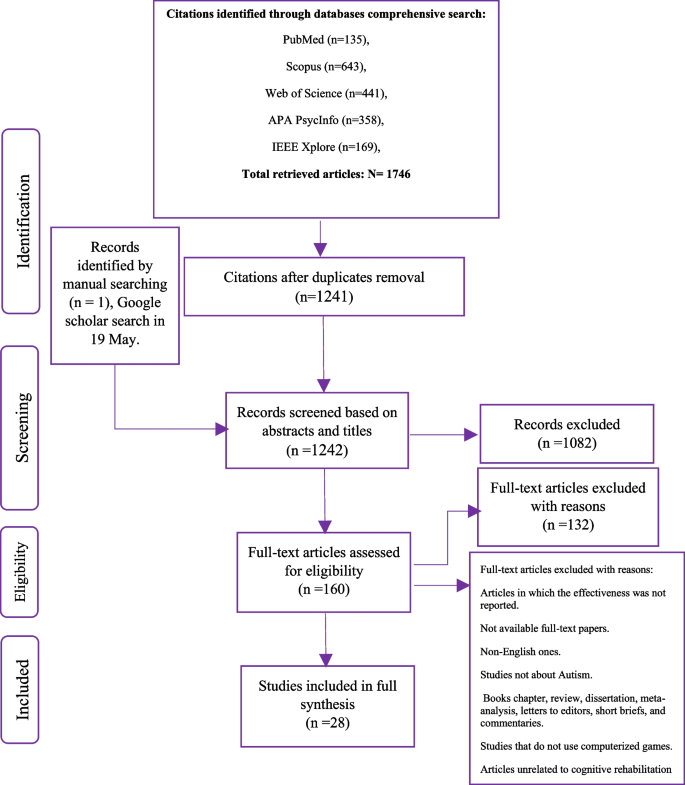
Features and effects of computer-based games on cognitive impairments in children with autism spectrum disorder: an evidence-based systematic literature review, BMC Psychiatry

The importance of low IQ to early diagnosis of autism - Denisova - 2023 - Autism Research - Wiley Online Library

Cognitive profiles of children with autism spectrum disorder with parent-reported extraordinary talents and personal strengths

Mathematical Skills in Autism Spectrum Disorder
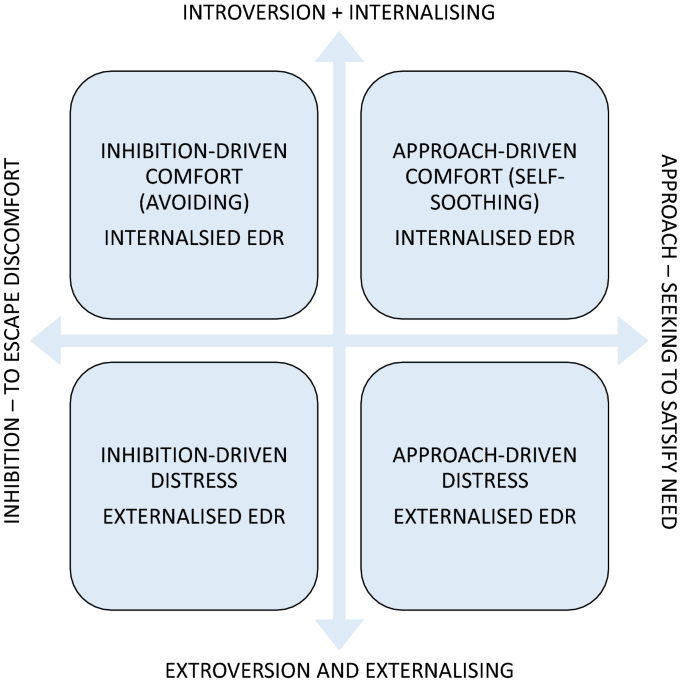
Underlying Thinking Pattern Profiles Predict Parent-Reported Distress Responses in Autism Spectrum Disorder

Easing the transition to secondary education for children with autism spectrum disorder: An evaluation of the Systemic Transition in Education Programme for Autism Spectrum Disorder (STEP-ASD) – topic of research paper in
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)