α-Synuclein Aggregation in Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
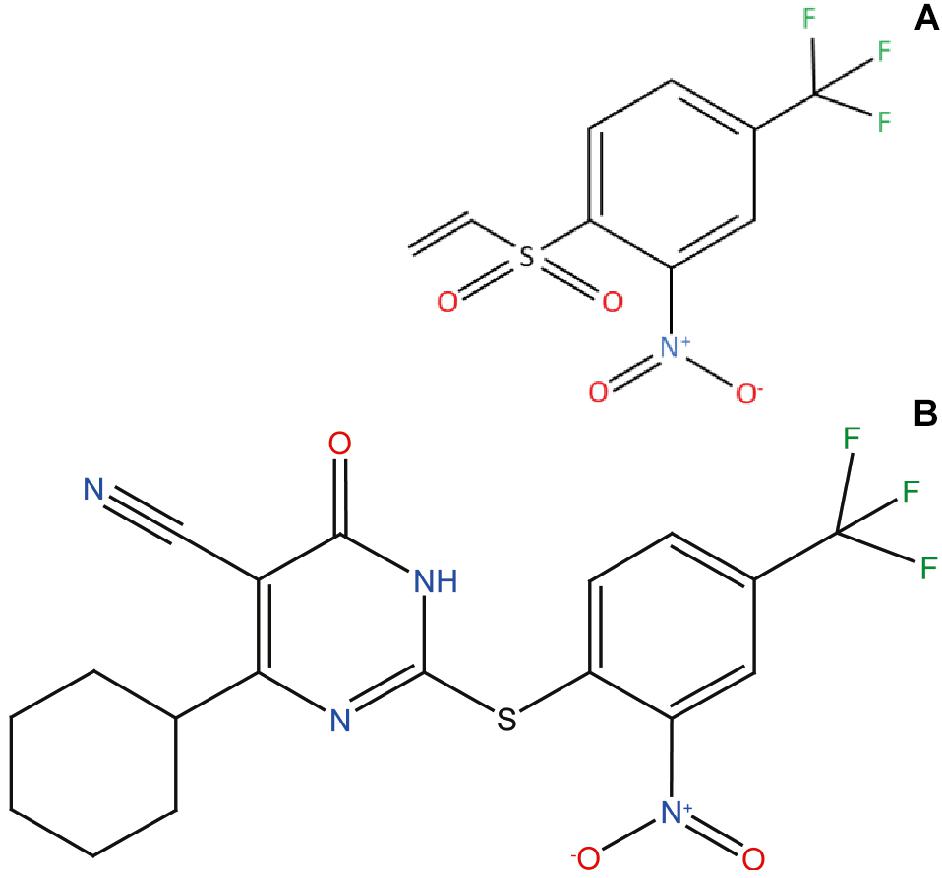
Parkinson’s disease, the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide, is characterized by the accumulation of protein deposits in the dopaminergic neurons. These deposits are primarily composed of aggregated forms of α-Synuclein (α-Syn). PD is a complex pathology initially associated with motor deficiencies, as a result of an acute neuronal loss in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc), with a significant dopaminergic (DA) impairment.

IJMS, Free Full-Text
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Active alpha-synuclein proteins

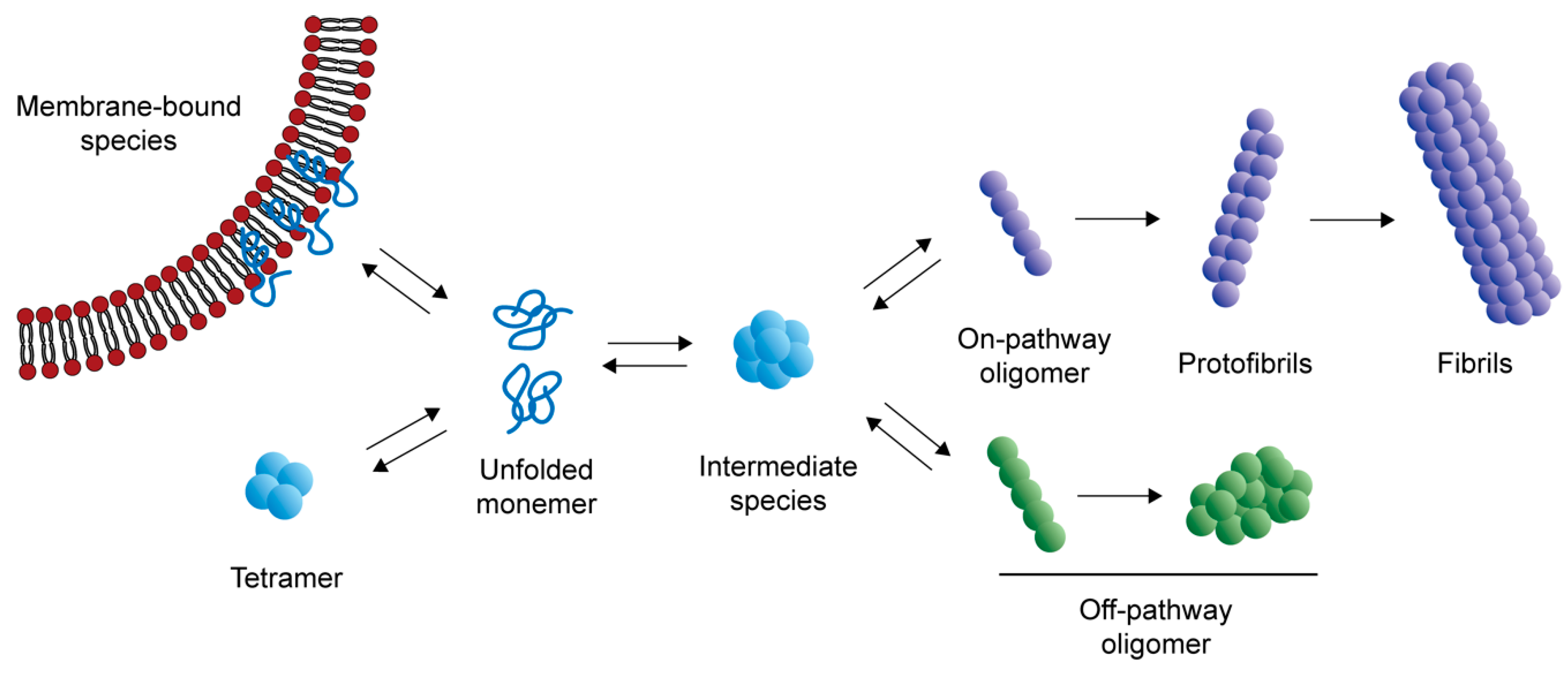
Clearance of α-Synuclein Oligomeric Intermediates via the Lysosomal Degradation Pathway

Tuning the Balance between Fibrillation and Oligomerization of α-Synuclein in the Presence of Dopamine
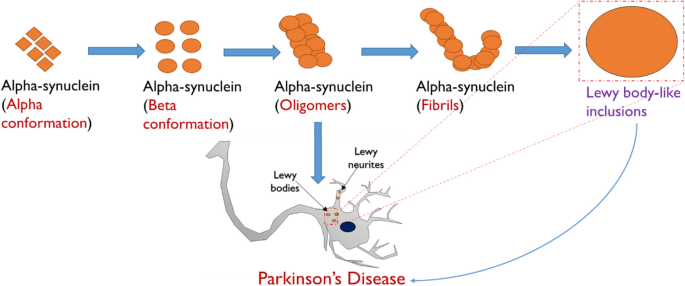
Diagnostic and therapeutic agents that target alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease
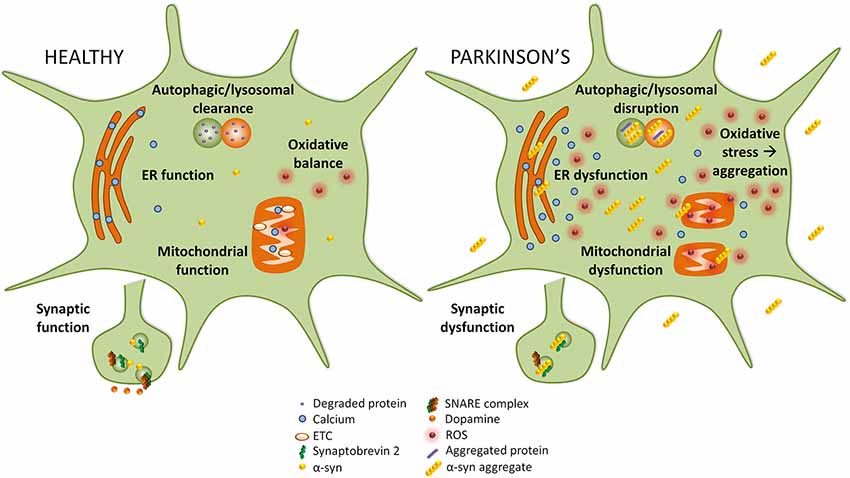
Frontiers Targeting Alpha-Synuclein as a Therapy for Parkinson's Disease
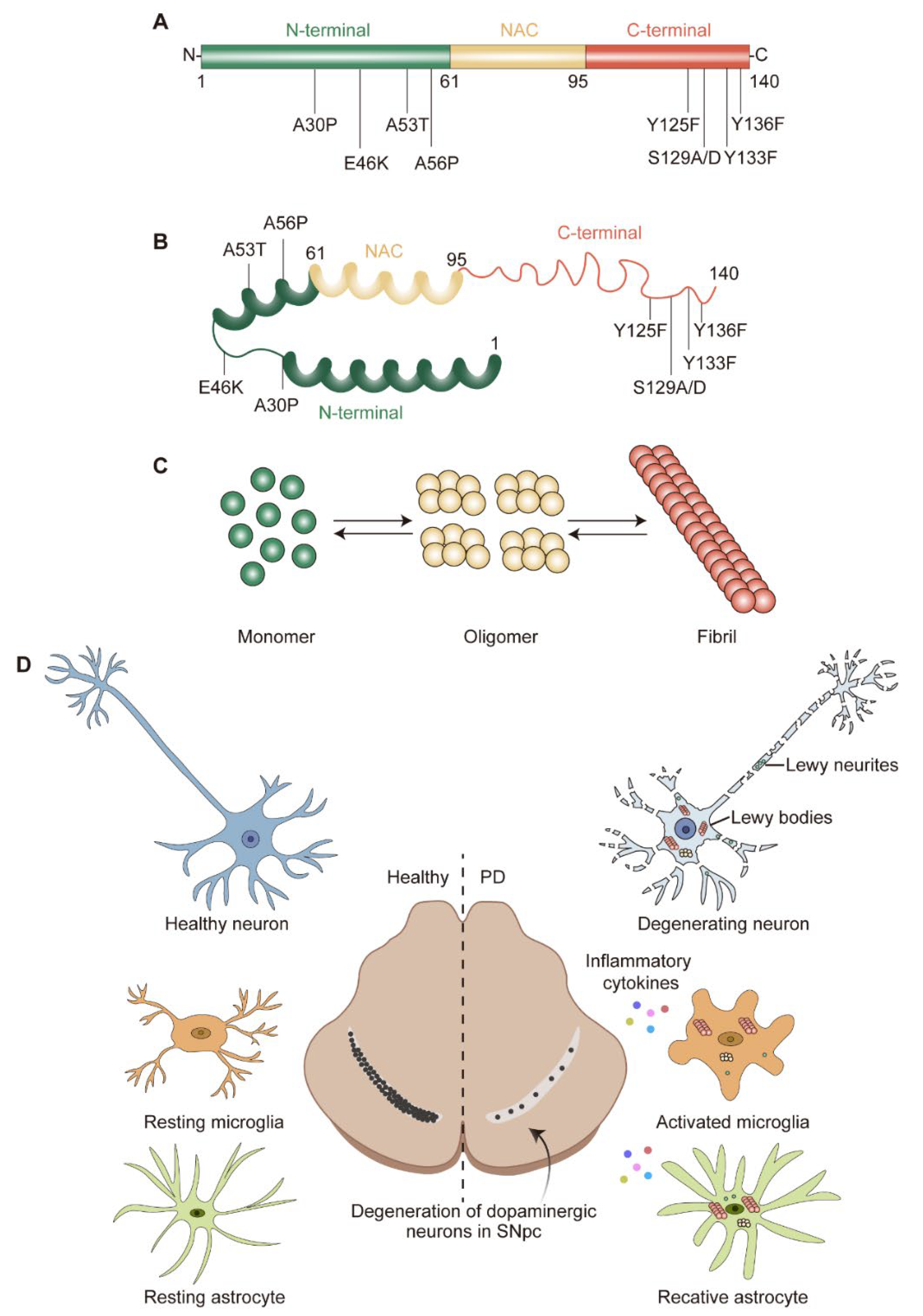
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Calcipotriol inhibits α‐synuclein aggregation in SH‐SY5Y neuroblastoma cells by a Calbindin‐D28k‐dependent mechanism - Rcom‐H'cheo‐Gauthier - 2017 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library
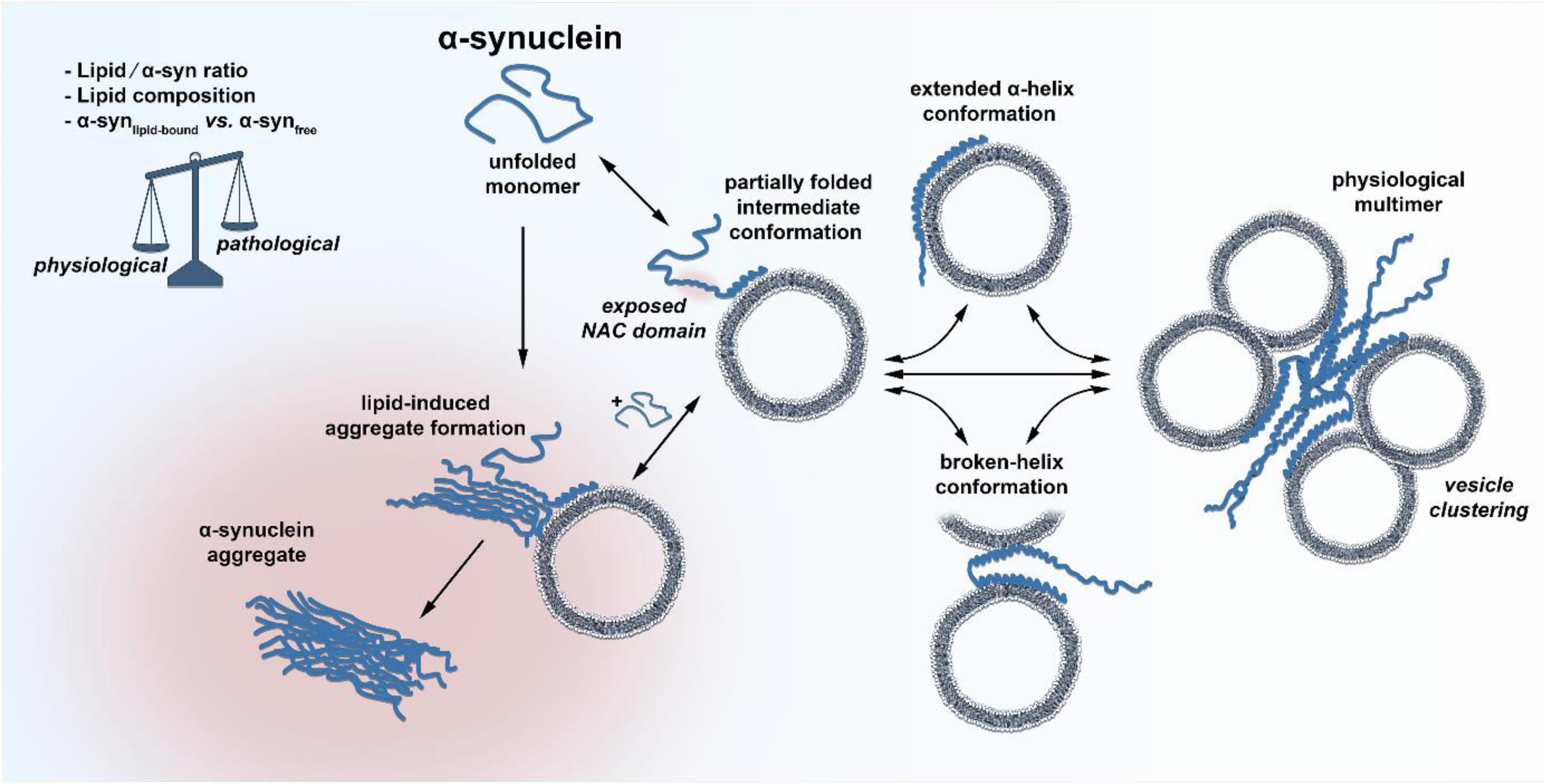
Frontiers The Role of Lipids in the Initiation of α-Synuclein Misfolding

Fast kinetics of environmentally induced α-synuclein aggregation mediated by structural alteration in NAC region and result in structure dependent cytotoxicity

PAP reduced α-synuclein expression and aggregation in MPTP/P-treated
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)