Theorem on Friends and Strangers; Why in Any Party of Six People, Either at Least Three of Them Are Mutual Friends, or at Least Three of Them Are Mutual Strangers
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Let’s take a look at Alice first. To her, each one of the other five (Bob, Carol, Dave, Ellen, and Frank) is either a friend or a stranger. Suppose Bob, Dave, and Frank are friends to Alice, and…

How Math Puzzles Help You Plan the Perfect Party

How to prove: at a party of six people either there are three mutual acquaintances or there are three mutual strangers - Quora

Correlation, Causation, and Ramsey Theory
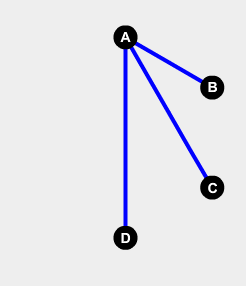
Theorem on Friends and Strangers. Ramsey Theory and Graham's Number, by Francesco Di Lallo

Correlation, Causation, and Ramsey Theory
New maths formula answers long-standing party problem
How to prove: at a party of six people either there are three mutual acquaintances or there are three mutual strangers - Quora

Party At Ramsey's

The Friendship Theorem - You Always Have 3 Friends Or 3 Strangers At A Party

This math puzzle will help you plan your next party

SOLVED: Prove this theorem: Among any six people, there exists a group of 3 mutual friends or a group of 3 mutual strangers. (Here friends and strangers are considered symmetric relations, i.e.

Party Problem The simplest example of Ramsey theory. It is also known as the 'Maximum Clique Problem'. A clique of a graph is a complete sub graph of the. - ppt download
How to prove: at a party of six people either there are three mutual acquaintances or there are three mutual strangers - Quora

Ramsey's Theorem: Friends and Strangers
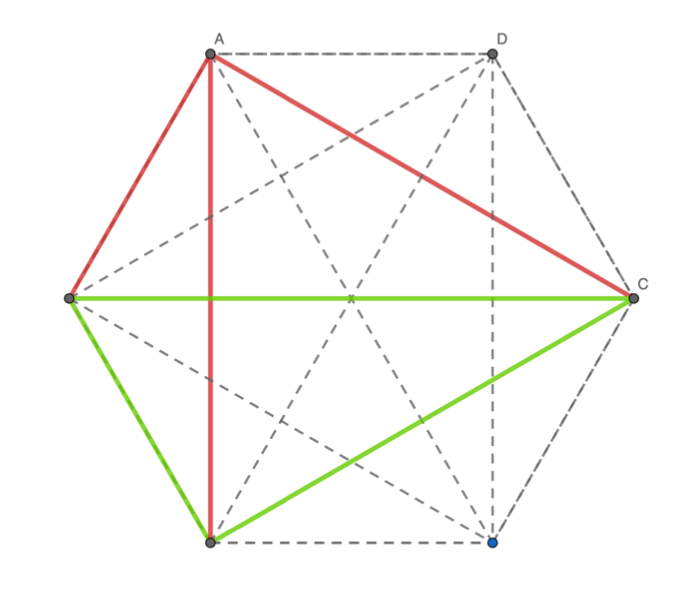
Ramsey Theorems in Euclidean Geometry — Math In Action
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







